前言
前段时间在使用 Zed 编辑器时,出现了 go lsp 启动错误,未能正确找到 go 语言的二进制文件。
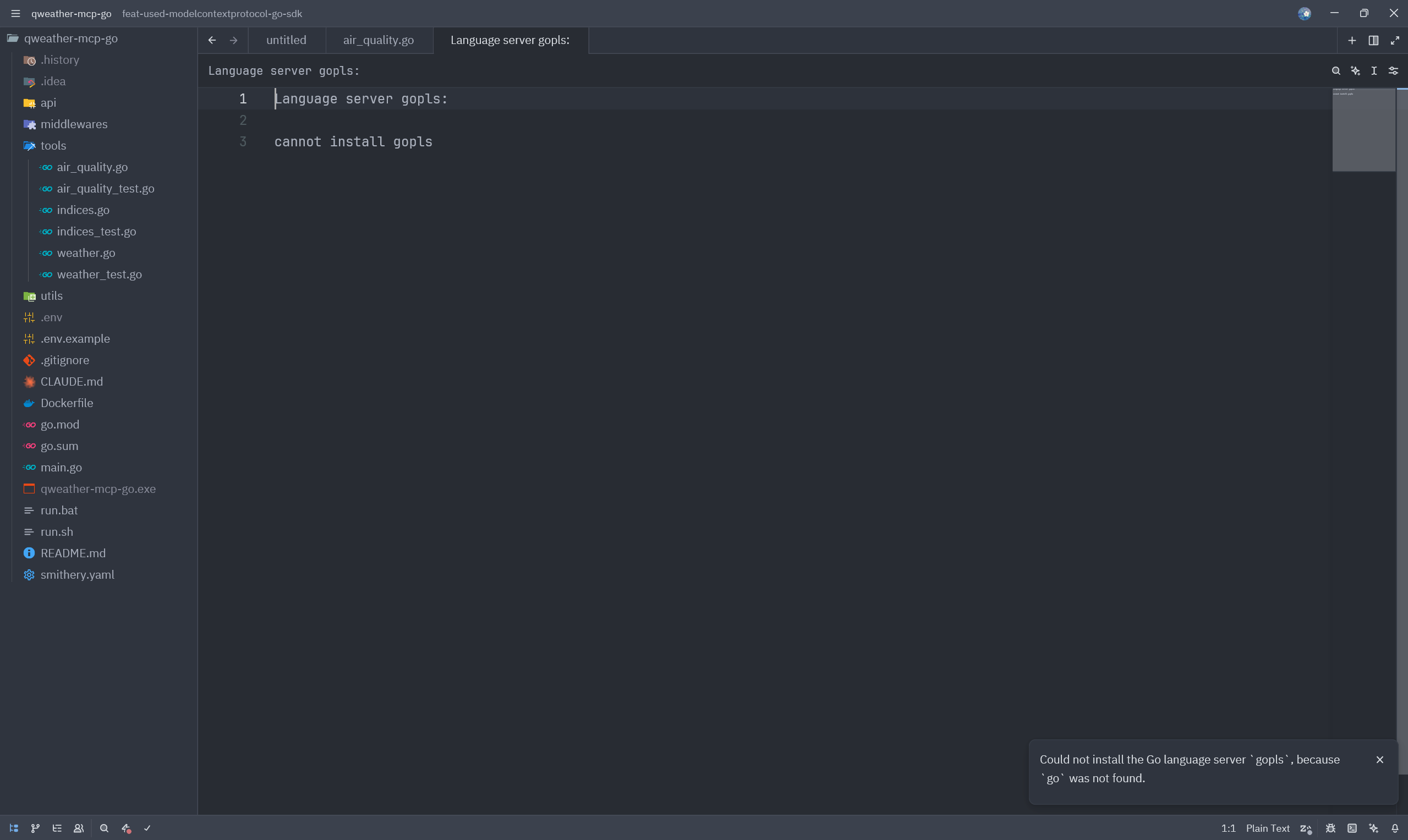
本文将一步步从源代码分析修复 Zed 的 go lsp 启动错误。
步骤
从错误信息可以得知,具体的逻辑在 /crates/languages/src/go.rs#L76,可以看到是 delegate.which("go".as_ref()).await.is_none() 方法的返回值为 true,导致 go 语言的二进制文件未找到。
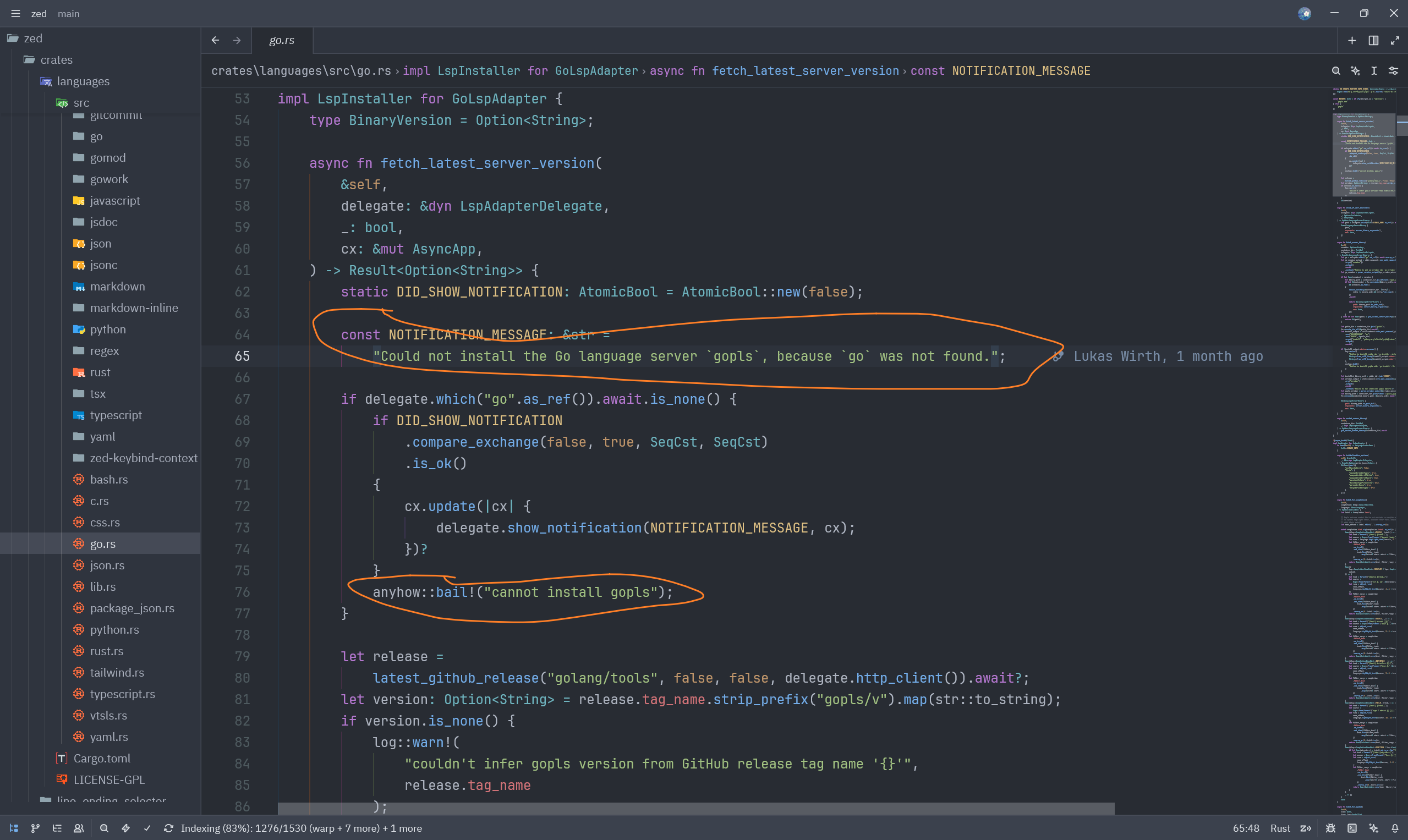
接下来寻找 which 方法的定义位置,可以看到是在 /crates/project/src/lsp_store.rs#L12758,这段代码实现了 LspAdapterDelegate trait 中的 which 方法,用于在系统中查找可执行文件的路径。

修改 which 方法,添加一些日志,以便更好地理解其执行过程。
async fn which(&self, command: &OsStr) -> Option<PathBuf> {
let mut worktree_abs_path = self.worktree_root_path().to_path_buf();
if self.fs.is_file(&worktree_abs_path).await {
worktree_abs_path.pop();
}
let shell_path = self.shell_env().await.get("PATH").cloned();
// Debug output
log::info!(
"which() called for command: {:?}, worktree_abs_path: {:?}, shell_path: {:?}",
command,
worktree_abs_path,
shell_path
);
let result = which::which_in(command, shell_path.as_ref(), worktree_abs_path).ok();
log::info!("which() result for {:?}: {:?}", command, result);
result
}
重新编译运行 Zed,查看日志:
[project::lsp_store] which() called for command: "gopls", worktree_abs_path: "D:\\code\\qweather-mcp-go", shell_path: None
2025-10-20T22:07:13+08:00 INFO [project::lsp_store] which() result for "gopls": None
2025-10-20T22:07:13+08:00 INFO [project::lsp_store] which() called for command: "go", worktree_abs_path: "D:\\code\\qweather-mcp-go", shell_path: None
2025-10-20T22:07:13+08:00 INFO [project::lsp_store] which() result for "go": None
可以看到 self.shell_env().await.get("PATH").cloned(); 的结果是 None 没有正确获取到环境变量。
继续为 shell_env 和 load_shell_environment 方法添加调试日志:
async fn load_shell_environment(
shell: &Shell,
dir: &Path,
load_direnv: &DirenvSettings,
) -> (
Option<HashMap<String, String>>,
Option<EnvironmentErrorMessage>,
) {
use crate::direnv::load_direnv_environment;
use util::shell_env;
if cfg!(any(test, feature = "test-support")) {
let fake_env = [("ZED_FAKE_TEST_ENV".into(), "true".into())]
.into_iter()
.collect();
(Some(fake_env), None)
} else if cfg!(target_os = "windows") {
let (shell, args) = shell.program_and_args();
log::info!(
"Windows: attempting to capture shell environment with shell={:?}, args={:?}, dir={:?}",
shell,
args,
dir
);
let envs = match shell_env::capture(shell, args, dir).await {
Ok(envs) => {
log::info!("Windows: successfully captured {} environment variables", envs.len());
if let Some(path) = envs.get("PATH") {
log::info!("Windows: captured PATH={:?}", path);
} else {
log::warn!("Windows: PATH not found in captured environment");
}
envs
}
Err(err) => {
log::error!("Windows: failed to capture shell environment: {:?}", err);
util::log_err(&err);
return (
None,
Some(EnvironmentErrorMessage(format!(
"Failed to load environment variables: {}",
err
))),
);
}
};
// Note: direnv is not available on Windows, so we skip direnv processing
// and just return the shell environment
(Some(envs), None)
} else {
let dir_ = dir.to_owned();
let (shell, args) = shell.program_and_args();
let mut envs = match shell_env::capture(shell, args, &dir_).await {
Ok(envs) => envs,
Err(err) => {
util::log_err(&err);
return (
None,
Some(EnvironmentErrorMessage::from_str(
"Failed to load environment variables. See log for details",
)),
);
}
};
// If the user selects `Direct` for direnv, it would set an environment
// variable that later uses to know that it should not run the hook.
// We would include in `.envs` call so it is okay to run the hook
// even if direnv direct mode is enabled.
let (direnv_environment, direnv_error) = match load_direnv {
DirenvSettings::ShellHook => (None, None),
DirenvSettings::Direct => match load_direnv_environment(&envs, dir).await {
Ok(env) => (Some(env), None),
Err(err) => (None, err.into()),
},
};
if let Some(direnv_environment) = direnv_environment {
for (key, value) in direnv_environment {
if let Some(value) = value {
envs.insert(key, value);
} else {
envs.remove(&key);
}
}
}
(Some(envs), direnv_error)
}
}
async fn shell_env(&self) -> HashMap<String, String> {
let task = self.load_shell_env_task.clone();
let result = task.await;
// Debug output
log::info!("shell_env() task result: {:?}", result.is_some());
if let Some(ref env) = result {
log::info!("shell_env() has {} variables", env.len());
if let Some(path) = env.get("PATH") {
log::info!("shell_env() PATH value: {:?}", path);
} else {
log::warn!("shell_env() loaded but PATH is missing!");
log::info!("Available env keys: {:?}", env.keys().collect::<Vec<_>>());
}
} else {
log::warn!("shell_env() task returned None - shell environment not loaded");
}
result.unwrap_or_default()
}
重新编译,通过日志,发现应该是跟环境变量的名称有关,在windows 上 path 变量的名称是 Path,而在其他操作系统上是 PATH。修改相关代码:
async fn which(&self, command: &OsStr) -> Option<PathBuf> {
let mut worktree_abs_path = self.worktree_root_path().to_path_buf();
if self.fs.is_file(&worktree_abs_path).await {
worktree_abs_path.pop();
}
let env = self.shell_env().await;
// On Windows, PATH might be "Path" instead of "PATH"
let shell_path = env.get("PATH")
.or_else(|| env.get("Path"))
.or_else(|| env.get("path"))
.cloned();
which::which_in(command, shell_path.as_ref(), worktree_abs_path).ok()
}
重新编译启动 zed,lsp error 已解决,并且提了 PR(#40711)。